Day-39 Part-1:☁Amazon EC2 User-Data🤵🏻📑
How to Use Amazon EC2 User Data to Automate Your Infrastructure Setup
📖 Introduction
In the last blog Getting Started with AWS Basics☁ we learned about the basics of AWS, What is IAM, Users*, **and User groups. We have also learned about Regions and Availability zones*, and we have performed some hands-on.
In this article, we are going to learn about the use of User data in AWS.
So let's get started...🏃♀️
🤔 What is Amazon EC2 User Data?
Amazon EC2 user data is a feature that allows you to pass metadata to your EC2 instances when they’re launched.
This metadata can be used to automate certain tasks, such as installing software packages, configuring settings, and running scripts.
User data is passed to your EC2 instances as plain text, and it’s automatically made available to your instance as a shell script. This means that you can use any scripting language you want to write your user-data script
💁 How to Use Amazon EC2 User-Data
To use Amazon EC2 user data, you’ll need to create a user data script. This script can be written in any scripting language you want, but we recommend using a shell script because it’s easy to get started with.
Here’s an example user-data script that installs the Jenkins on an EC2 instance:
✍ Create the Script File:
Here is the shell script file to install the Jenkins on the EC2 instance using user data.
This script updates the package manager, downloads the required key and package, installs Jenkins, enables Jenkins, and starts automatically on boot.
#!/bin/bash sudo apt-get update -y sudo apt install openjdk-11-jre -y curl -fsSL https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io-2023.key | sudo tee \ /usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc > /dev/null echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc] \ https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ | sudo tee \ /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list > /dev/null sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install jenkins -y sudo systemctl enable jenkins sudo systemctl start jenkins
✈️ Launch EC2 Instance:
Go to EC2 > Instance and click on Create instance. Provide the required configuration.
Now this is the place where we need to add your script data. Expand the Advanced Details tab. Add the script or choose the file in the User data section and click on the launch instance.
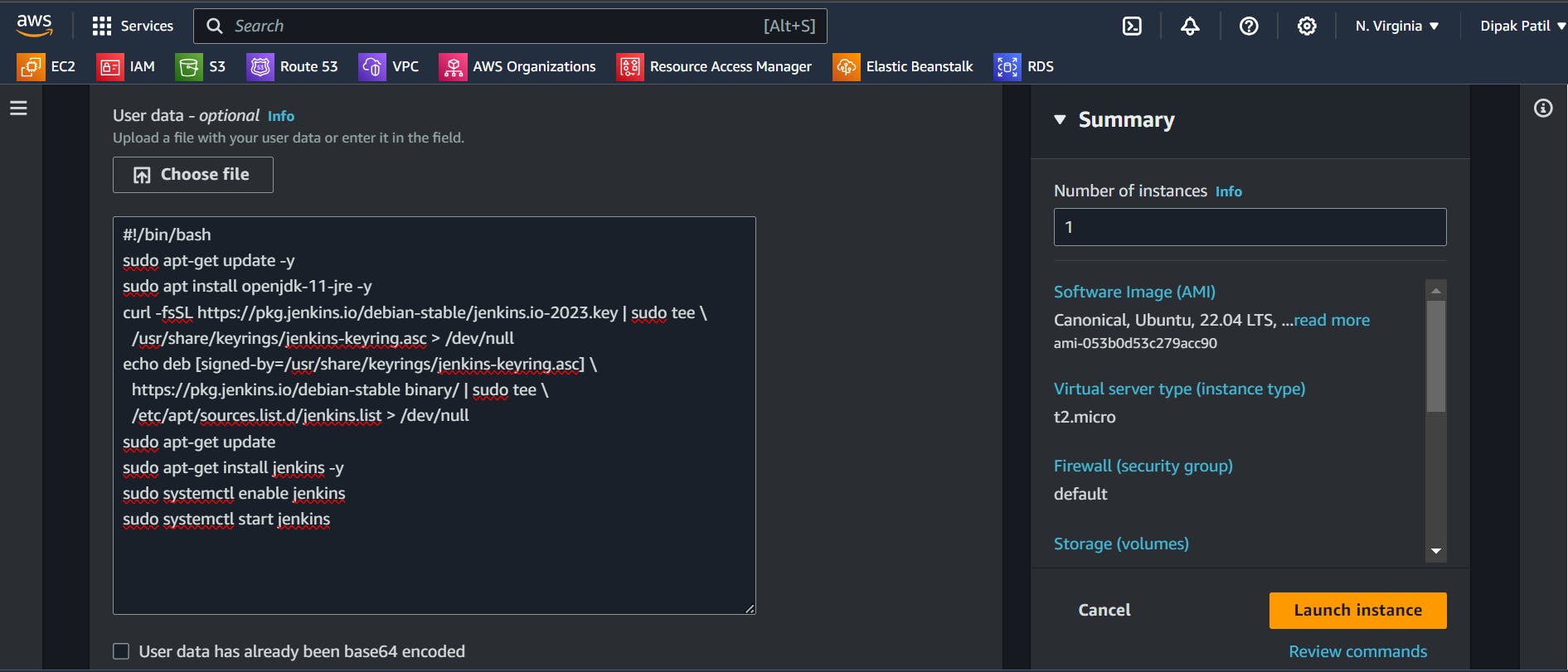
✅ Verify the installation:
Connect the instance and verify the installation using the command.
jenkins --version systemctl status jenkins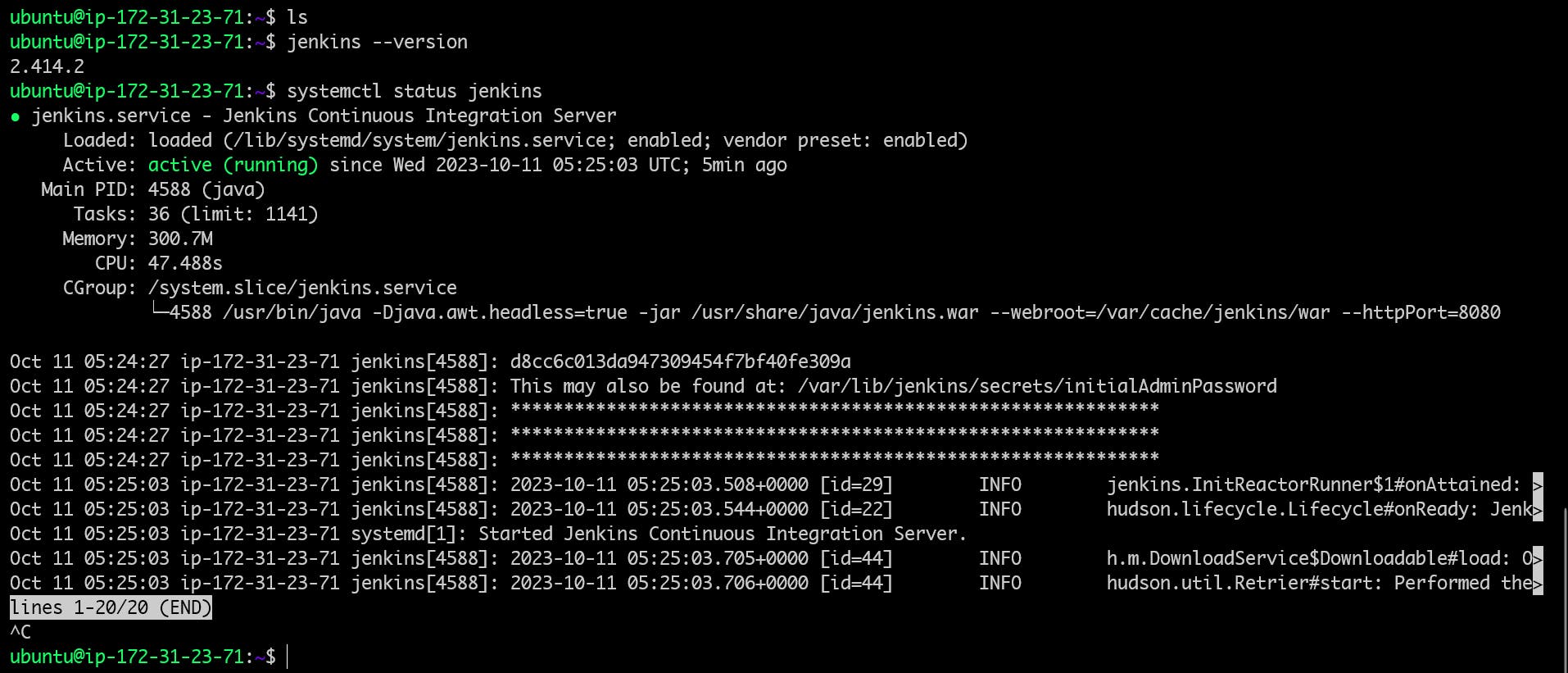
Make sure the port
8080should open in your EC2 instanceSecurity Groupbecause Jenkins runs on port 8080.Go to the browser and type EC2 instance public IP followed by port 8080
<EC2-Public-IP>:8080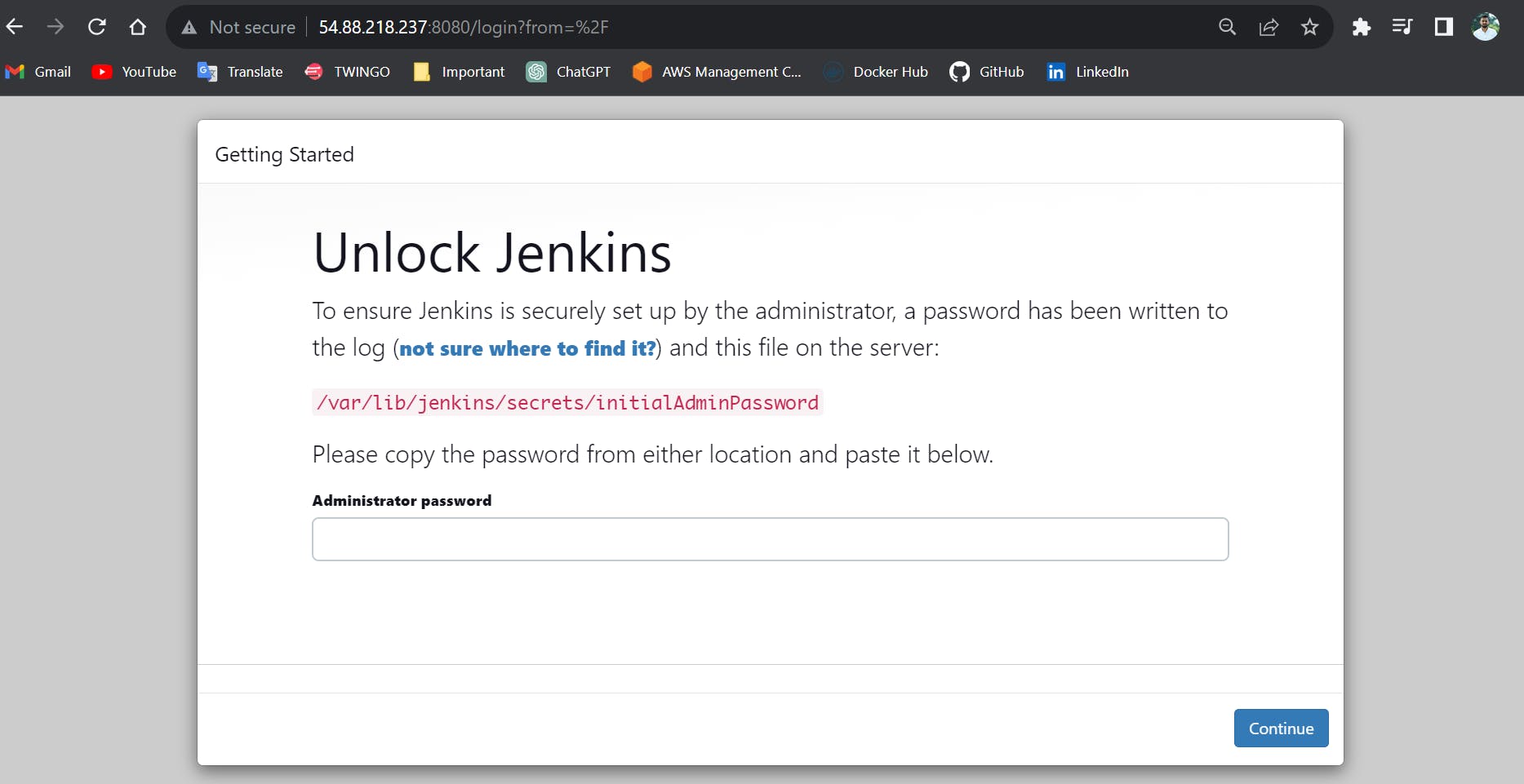
We can see the Jenkins page is visible means we successfully installed the Jenkins on EC2 instance using User data at the time of launch Instance.
⚖️ Conclusion
Amazon EC2 user data is a powerful feature that allows you to automate your infrastructure setup. By passing metadata to your EC2 instances as plain text, you can use any scripting language you want to automate tasks like installing software packages, configuring settings, and running scripts.
In this blog post, we’ve explained what user data is, how it works, and how you can use it to automate your infrastructure setup. We’ve also provided an example user-data script that installs the Apache web server on an EC2 instance.
If you’re looking to automate your infrastructure setup, Amazon EC2 user data is a great place to start. Give it a try and see how it can help you streamline your workflow and save time.
