Introduction
In this blog post, we will walk you through the Helm in K8s. We will learn how we can package our Kubernetes resources and how we can deploy the application using K8's package manager Helm.
💼 What is Helm in K8's?
Helm is a package manager for Kubernetes applications. It simplifies the process of defining, installing, and upgrading even the most complex Kubernetes applications. Essentially,
Helm allows you to define your Kubernetes applications as charts.
A Helm chart is a collection of pre-configured Kubernetes resources, which can be versioned, shared, and deployed as a single unit.
Helm provides templating, allowing you to parameterize your Kubernetes manifests and create dynamic, reusable configurations.
🤔 Why We Need Helm?
Helm solves several challenges in the Kubernetes deployment process:
Simplified Deployment: Helm packages Kubernetes manifests into a single unit, making it easier to manage and deploy complex applications.
Versioning and Rollbacks: Helm enables versioning of your applications, allowing you to roll back to previous versions if new deployments cause issues.
Templating: Helm's templating engine enables the dynamic generation of Kubernetes manifests, making it easy to customize deployments for different environments or use cases.
Collaboration: Helm charts can be shared via Helm repositories, making collaboration among developers and promoting the sharing of best practices.
🧩 Helm Components
Here are the components of the Helm.
Chart: A Helm package that contains pre-configured Kubernetes resources.
Values.yaml: A file where users can define customizable parameters for their charts.
Templates: Kubernetes manifest files with Helm-specific templating.
Release: A deployed instance of a Helm chart.
Repository: A collection of pre-packaged charts that users can fetch from.
🏛 Helm Architecture

As we we know we are interacting with our K8's cluster with the help of Kubectl CLI which communicates with the Kube API server and proceeds with the rest of the things.
Now to work with helm command, Helm internally communicates with Kubectl CLI so that the helm chart can understand which Kubernetes cluster it is interacting with
📌 Real-World Example
Imagine you are managing a microservices-based application with multiple services that need to be deployed and scaled independently. Helm allows you to create charts for each service, define their dependencies, and manage their deployments as a cohesive application. When you need to update a service or roll back to a previous version due to issues, Helm simplifies the process, making your DevOps tasks more efficient and error-free.
Helm is a valuable tool in the DevOps toolbox, streamlining Kubernetes deployments and making it easier to manage complex applications in a containerized environment.
🛠️ Helm Installation
📜 Prerequisites
Kubernetes cluster: You should have a Kubernetes cluster up and running.
To install Helm use the below command in your system.
curl https://baltocdn.com/helm/signing.asc | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/helm.gpg > /dev/null sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https --yes echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/helm.gpg] https://baltocdn.com/helm/stable/debian/ all main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/helm-stable-debian.list sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install helm helm version
📄 Basic helm command
Create helm chart:
Create the helm chart directory with some predefined YAML files and folders like
Chart.yaml, values.yaml, templates folder, deployment.yaml, ingress.yaml, service.yaml, serviceaccount.yaml etc.#helm-chart-name can be anything as per your convenient helm create <helm-chart-name>Install helm chart:
Note: The
helm installcommand takes two arguments -First argument - Release name that you pick.
Second argument - Chart you want to install(typically directory you created using helm create command).
helm create <release-name> <chart-name>
Helm chart list
List of all installed helm charts.
helm list -aHelm chart directory structure:
Use to view helm chart directory structure after creating helm chart.
tree <actual-chartname>Helm Upgrade:
If you made any changes in the helm chart you need to upgrade your helm chart to reflect the changes.
helm upgrade <release-name> <chart-name>Helm Rollback:
If you want to switch to your previous version of the helm chart you need to use the helm rollback command.
Note: To rollback you need to specify the revision number of the helm chart.
helm rollback <release-name> <revision-number>Helm debug and dry-run:
Use it to validate your helm chart before installation.
helm install <release-name> --debug --dry-run <chart-name>Helm template:
Renders the chart templates locally which means it validates the helm chart templates.
#actual-helchart-name is the name of your chart #which is created after hitting the helm create command helm templete <actual-helchart-name>Helm Lint:
Use it to find any errors or misconfigurations with the helm chart.
#actual-helchart-name is the name of your chart #which is created after hitting the helm create command helm lint <actual-helchart-name>Helm uninstall:
Use to uninstall/remove the helm chart.
helm uninstall <helchart-name>To know more about the helm command visit the official helm site.
🚀 Running Reddit Clone using Helm Charts
📜 Prerequisites:
Kubernetes cluster: You should have a Kubernetes cluster up and running.
Helm: Helm should be installed on your local machine.
📝Create a Helm Chart:
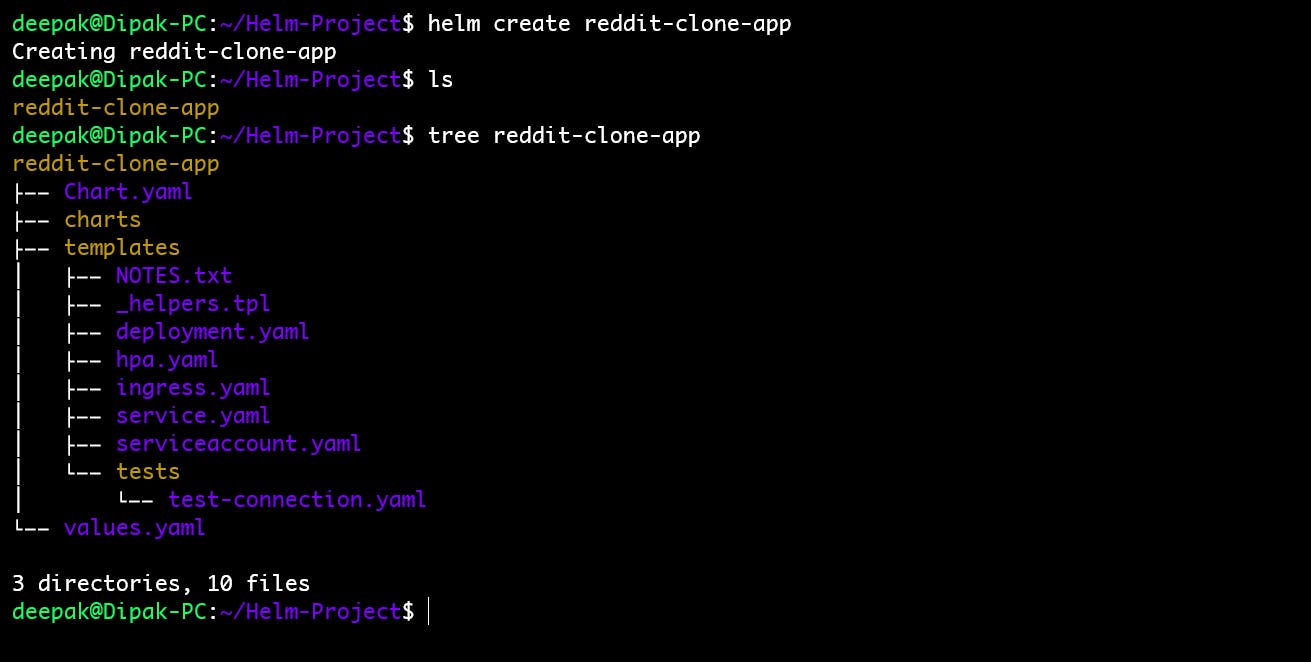
First, we need to create a Helm chart to define the deployment of our application. Open your terminal and run the following command to create a Helm chart.
This command generates a directory structure for your Helm chart with default templates and values.
📝Edit values.yaml:
Navigate to the "node-app" directory open the
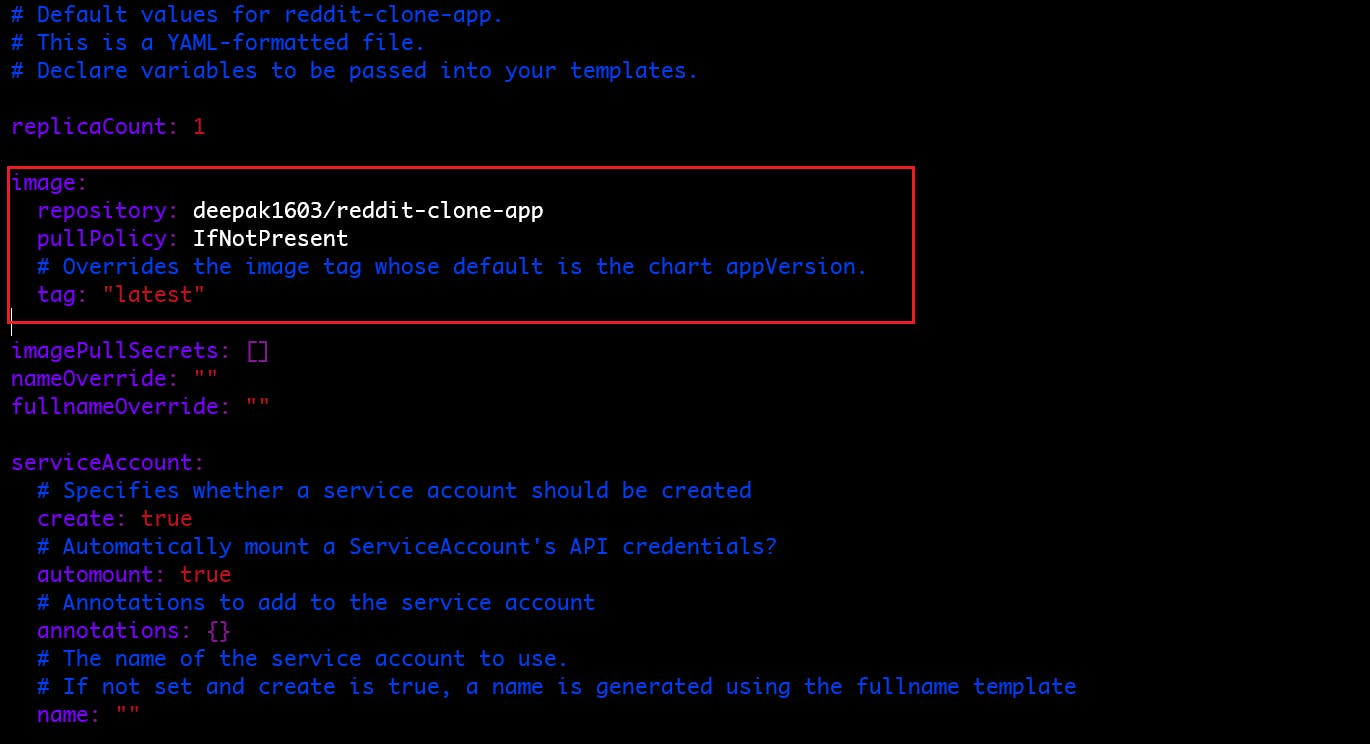
values.yamlfile and update the values as per your requirement.values.yaml: This configuration specifies the number of replicas, Docker image details, and service and other specifications for your application.
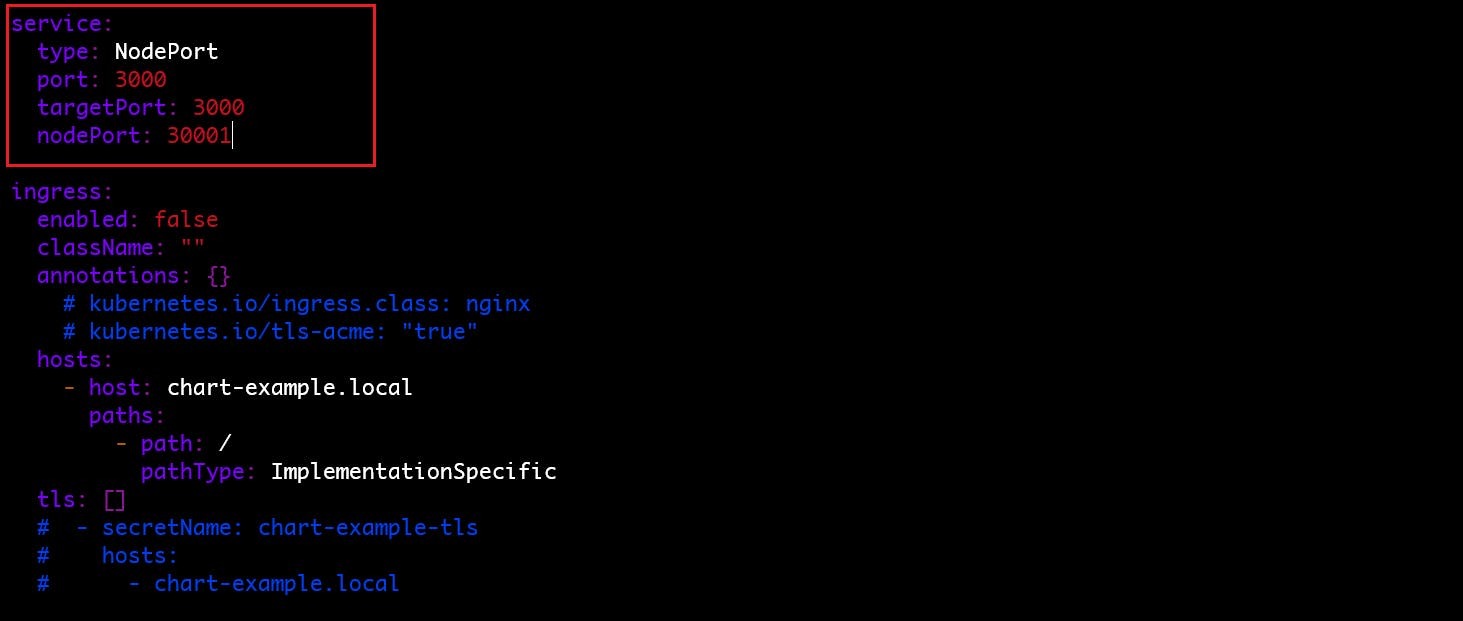
Here we replace the image attribute where we will specify the repository as our docker hub image and tag and Service as a NodePort service.
🔰 Deploy Helm Chart:
To deploy the Helm Chart use the command
helm install <helm-chart-release-name> ./<actual-helm-chart-name>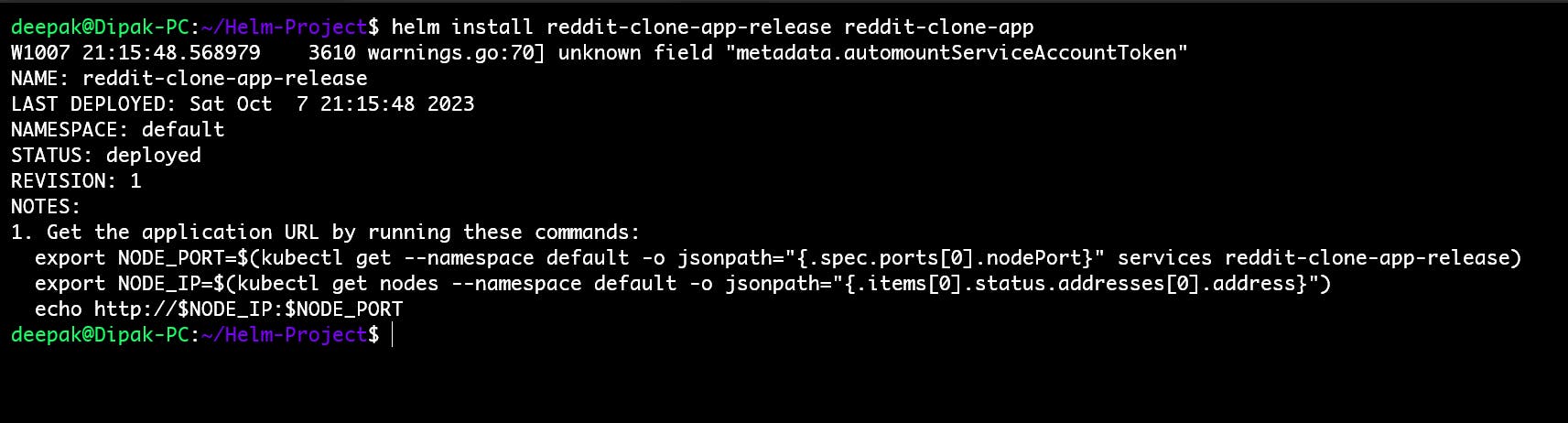
✅ Verify Helm Chart In:
To verify helm chart installation use the command.
helm list -a
You can see our helm chart installation done successfully with Revision Number 1.
✅ Verify the Deployment & Service:
To verify that your application has been deployed successfully, you can run the following command to list all the deployments in your cluster.
kubectl get deployments kubectl get service kubectl get pod or kubectl get all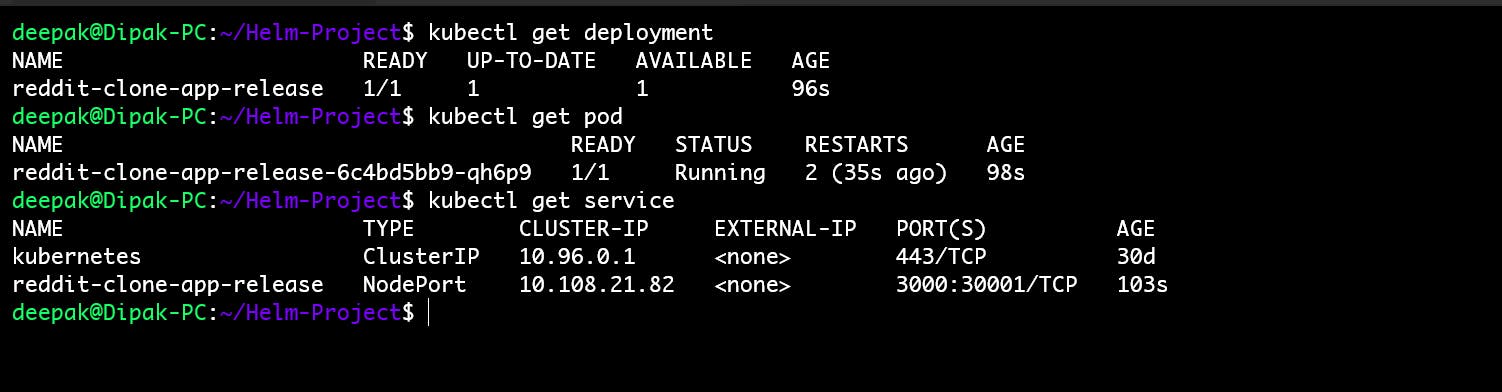
🌐 Access the Application:
You can now access your application by visiting the URL provided by Minikube.
minikube service <service-name> -- url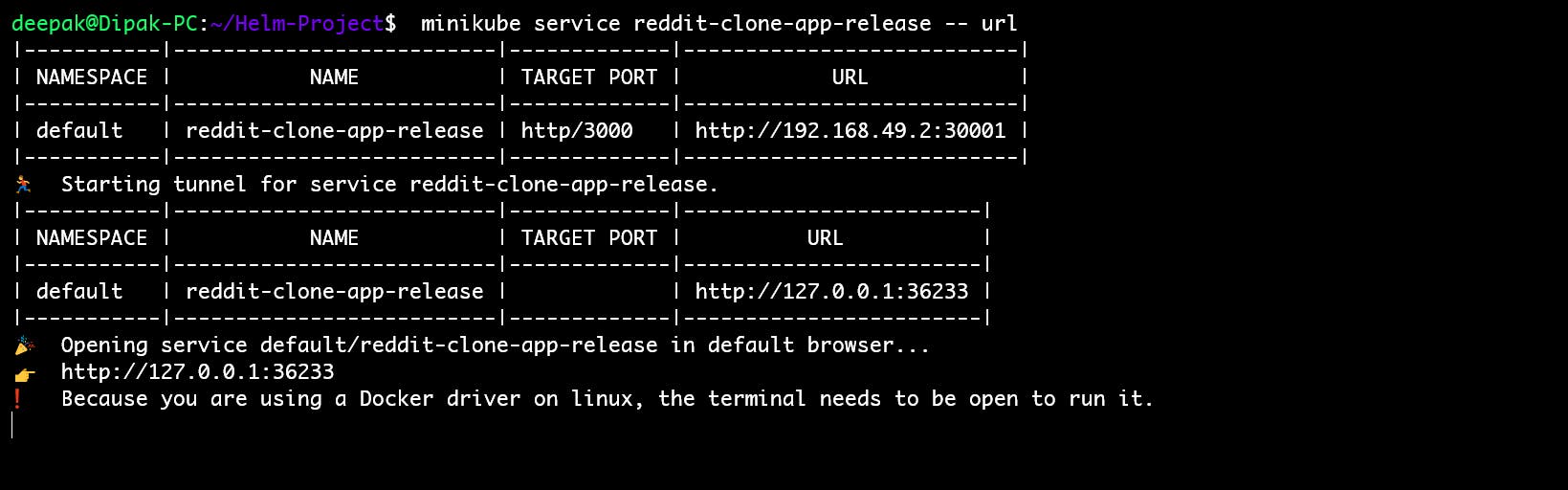
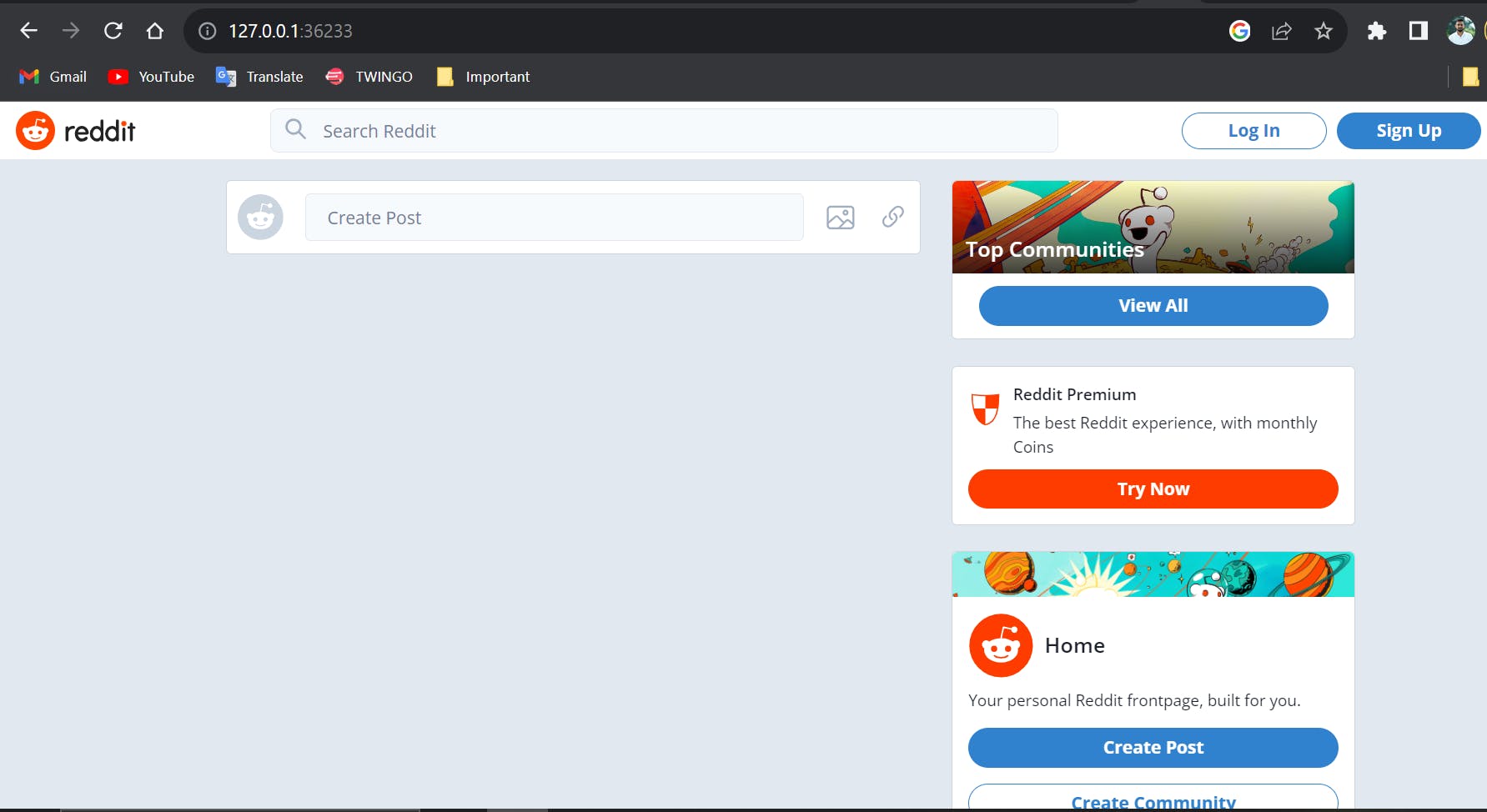
🎉 Congratulations! You have successfully deployed a Reddit Clone Appl using Helm. Helm makes it easy to define and manage complex Kubernetes deployments, making it an essential tool for DevOps engineers working with Kubernetes.
📝 Summary
- In summary, Helm is essential for simplifying the management and deployment of Kubernetes applications. Its ability to package, version, template, and share applications enhances collaboration, consistency, and scalability in Kubernetes environments.
Thank you🙏🙏... for taking the time to read this blog. I hope you found the information helpful and insightful. So please keep yourself updated with my latest insights and articles on DevOps 🚀 by following me on
So, Stay in the loop and stay ahead in the world of DevOps!
Happy Learning !... Keep Learning ! 😊
